カージオイド
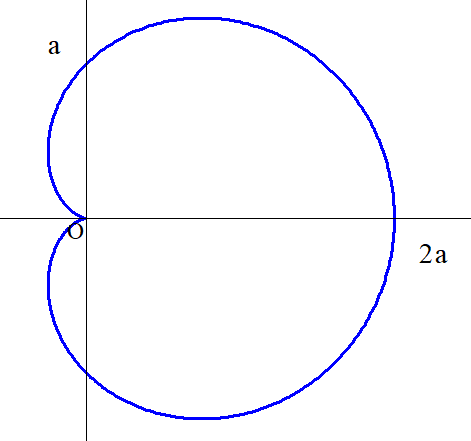
$極座標で \ \ r=a(1+\cos \theta)\ \ と表される図形をカージオイドといいます。$
$\qquad 詳しくは($カージオイド$)をご覧ください。$
$この図形の囲む領域の面積を求めてみましょう。対称性は明らかだから$
\begin{eqnarray*}
S
&=&2 \times \cfrac{1}{2} \int _0^{\pi} r^2 d\theta\\
\\
&=&\int _0^{\pi} a^2(1+\cos \theta )^2 d\theta \hspace{3em} (\cos \theta=2\cos ^2 \cfrac{\theta}{2}-1 \quad だから)\\
\\
&=&a^2 \int _0 ^{\pi} 4\cos ^4 \cfrac{\theta}{2} d\theta \hspace{4em} (\cfrac{\theta}{2}=t \quad とおくと \quad d\theta=2dt)\\
\\
&=&4a^2 \int _0 ^{\scriptsize{\cfrac{\pi}{2}}} \cos ^4 t \cdot 2dt \\
\\
&=&8a^2 \cdot \cfrac{3}{4} \cdot \cfrac{1}{2} \cdot \cfrac{\pi}{2}\\
\\
&=&\cfrac{3}{2}\pi a^2
\end{eqnarray*}
$\qquad この定積分の値の求め方は \ \ $$\int_{0}^{\scriptsize{\cfrac{\pi}{2}}}\sin^m x \cos ^n xdx$ $\ \ をご覧ください$
$なお、この定積分は次のように直接求めることもできます。$
\begin{eqnarray*}
S
&=&a^2 \int _0 ^{\pi} (1+\cos \theta)^2 d\theta \\
\\
&=&a^2 \int _0 ^{\pi} (1+2\cos \theta +\cos ^2 \theta)d\theta \\
\\
&=&a^2 \int _0 ^{\pi} (1+2\cos \theta +\cfrac{1+\cos 2\theta}{2})d\theta \\
\\
&=&a^2 \big[\cfrac{3}{2}\theta+2\sin \theta +\cfrac{\sin 2\theta}{4}\big]_0^{\pi}\\
\\
&=&\cfrac{3}{2}\pi a^2
\end{eqnarray*}
極座標表示による曲線の囲む面積
メインメニュー に戻る